Table of Contents
Bed Bug Guide for Landlords & Homeowners
Intended for self-diagnosis or as a substitute for consultation. If you have any questions about the disease described above or think that you may have an infection, consult with your doctor.
Because bed bug bites affect everyone differently, some people may have no reaction, and will not develop bite marks or other visible signs of being bitten. Other people may be allergic to bed bugs and can react adversely to the bites.
These allergic symptoms can include enlarged bite marks, painful swelling at the bite site and, on rare occasions, anaphylaxis. It may be difficult to tell if a bed bug has bitten you unless you find the bed bugs or signs of infestation.
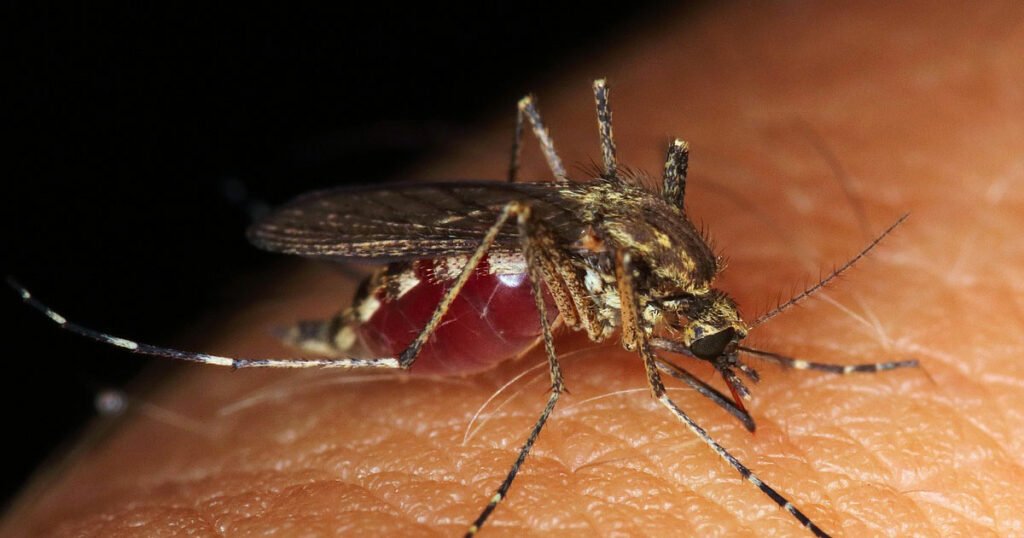
When bed bugs bite, they inject an anaesthetic and an anticoagulant that prevents a person from realizing they are being bitten. Most people do not know they have been bitten until the bite mark appears days afterwards.
The bite marks are similar to that of a mosquito or a flea. It may be a slightly swollen and red area that may itch and be irritating. Bite marks may be in a straight line or be random. Other bites symptoms may include insomnia, anxiety, and skin problems arising from the bites’ profuse scratching.
What are bed bugs?
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, flat, parasitic insects that feed solely on the blood of people and animals while they sleep. They are reddish-brown in colour, flat, have six legs, are wingless, range from 1mm to 7mm (about the size of an apple seed), and can live several months without a blood meal.
They will be a more rusty red colour after feeding. Bed bugs are nocturnal in nature. They usually feed during the night, with peak biting/feeding generally taking place just before dawn. They can obtain their meal in as little as 3 minutes and then drop off and hide to digest their meal.
Where do bed bugs come from?
Bed bugs are found across the globe. Although the presence of bed bugs has traditionally been seen, as a problem in developing countries, it has recently been spreading rapidly in parts of the United Kingdom, and other parts of Europe.
Bed bugs have been found, in 5-star hotels, and their presence is not determined, by the cleanliness of the living condition where they are found. Bed bug infestations usually occur around or near the areas where people sleep.
They hide during the day in places such as seams of mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, dresser tables, inside cracks or crevices, behind wallpaper or any other clutter or objects around a bed. They have been shown, to be able to travel over 100 feet in a night but tend to live within 8 feet of where people sleep.
Adults and all nymph stages of bed bugs need to take blood meals from warm-blooded hosts, which are typically humans, although other mammals and birds can be utilized for feeding in the absence of a human host.
Females will lay about five eggs daily throughout their adult lives in a sheltered location (like a mattress seam, crevices in a box spring, or space under a baseboard). Eggs hatch in about 4-12 days into the first stage of nymph.
The nymph goes through 5 stages each requiring a blood meal to develop into an adult. Mating occurs off of the host. Adults live 6-12 months and may survive for long periods of time without feeding.
What are the symptoms of bed bugs?
One of the easiest ways to identify a bed bug infestation is by the bite marks on the face, neck, arms, hands, or any other body parts. However, these bite marks may take as long as 14 days to develop in some people, so it is essential to look for other clues when investigating if bed bugs have infested an area. These signs include:
The bed bugs’ exoskeletons after moulting Bed bugs in the folds of mattresses and sheets Rusty coloured blood spots due to their blood-filled faecal material that they excrete on the bedding or nearby furniture a sweet, musty odour.
Because bed bug bites affect everyone differently, some people may have no reaction and will not develop bite marks or other visible signs of being bitten. Other people may be allergic to the bed bugs and can react adversely to the bites. These allergic symptoms can include enlarged bite marks, painful swelling at the bite site and on rare occasions, anaphylaxis.
It may be hard to tell if you have been bitten by a bed bug unless you find the bed bugs or signs of infestation. When bed bugs bite, they inject an anaesthetic and an anticoagulant that prevents a person from realizing they are being bitten.
Most people do not know they have been bitten until the bite mark appears days afterwards. The bite marks are similar to that of a mosquito or a flea. It may be a slightly swollen and a red area that may itch and be irritating. Bite marks may be in a straight line or be random. Other symptoms of bites may include insomnia, anxiety, and skin problems that arise from the profuse scratching of the bites.
How soon do symptoms of bed bugs appear after exposure?
Marks may take as long as 14 days to develop in some people.
How are bed bugs spread?
Because bed bugs can be found in homes and a variety of public places, they can easily be transported from place to place by people. They can hide in the seams of luggage, overnight bags, bedding, and in the folds of clothing.
They can also be transported in furniture. Most people do not realize they are transporting bed bugs as they travel from location to location, infecting areas as they go. Bed bugs are experts at hiding, can stay hidden for long periods of time, and can stay alive even without a blood meal.
How are bed bug bites diagnosed?
Although most people do not realize they have been bitten by a bed bug until bite marks appear (which can be as long as 14 days after the bite), finding a bite mark is the easiest way to identify a bed bug infestation.
A bed bug infestation is apparent by noticing black or brown spots (which is from their faecal waste) on surfaces. Sometimes the eggs, eggshells, and exoskeletons of the bed bug can be found in their hiding places.
Are there long-term complications of a bed bug infestation?
Bed bugs should not be considered a medical or public health hazard. Bed bugs are not known to spread disease. They can be an annoyance because of their itching and loss of sleep. Itching, which can lead to excessive scratching, can increase the chance of a secondary skin infection.
Although bed bugs are not considered to be dangerous, an allergic reaction to several bites may need medical attention.
How are bed bug bites and infestations treated?
Bed bug bites usually do not pose serious health or medical threat. The best way to treat a bite is to avoid scratching the area and apply antiseptic creams or lotions and take an antihistamine. Minimal treatment and good hygiene to prevent itching and secondary infections are usually sufficient treatment for most cases of bed bug bites.
If you suspect you are having an allergic reaction to bed bug bites contact your physician. In severe cases, topical steroid creams, antihistamines, topical antiseptics, or antibiotics may need to be given in the case of a secondary infection.
Bed bug infestations are commonly treated by insecticide spraying. If you suspect you have an outbreak, contact your landlord or a professional pest control company that is experienced with treating bed bugs.
It usually takes multiple visits by a licensed pest control operator to successfully treat a bed bug infestation. Over the counter foggers and pesticides will not eliminate bed bugs. Early detection and efficient treatment are crucial for the control of bed bugs.
Prior to treatment by an exterminator:
The home/apartment should be cleaned, organized, and free of clutter. Caulk and seal crevices around the room and on furniture. Seal any spaces between floors and baseboards.
Seal items in plastic bags or airtight containers. Store these outside the apartment or home for at least six months to ensure re-infestation does not occur. Remove all bed linens (including blankets, bed skirts), stuffed animals, pillows, and drapes.
Launder these items in hot water and the highest dryer setting. If needed, dry clean items. Move furniture away from walls. Apply a high knee stocking over the vacuum wand then vacuum entire area including mattress, furniture and baseboards. Place the mattress and box spring in a sealed plastic mattress cover bag and store away from home for six months to 1 year.
Remove the stocking from the vacuum and discard immediately in a sealed plastic bag. If any furniture is discarded, be sure to paint on it that it is infested with bed bugs to prevent others from taking items into their homes.
Who gets bed bugs?
Everyone is at risk of getting bed bugs when visiting an infected area. Anyone who travels frequently and shares living and sleeping quarters where other people have previously slept has a higher risk of being bitten and or spread a bed bug infestation.
How long can a person carry bed bugs?
Bed bugs can continue to live in areas of infestation as long as they are reproducing and are able to feed periodically on humans if they are not treated by a pest control professional. They do not live on humans, but they get on humans to feed.
It usually takes multiple visits by a licensed pest control operator who has experience in the elimination of bed bugs. Over the counter foggers and pesticides will not eliminate bed bugs. Unless the source is excluded from the property, the bed bugs will continually replenish, and the life cycle will continue.
How common are bed bugs?
Bed bugs are not a notifiable condition, so the magnitude of bed bug infestations is not known. But it is known they are a resurging problem causing property loss, expense, and inconvenience.
Bed bugs are found across the globe from North and South America to Africa, and Europe. Although the presence of bed bugs has traditionally been seen as a problem in developing countries, it has recently been spreading rapidly in parts of the United States, the United Kingdom, and other parts of Europe.
How can bed bugs be prevented?
The best way to prevent bed bugs is regular inspection for the signs of an infestation. Hotel staff should inspect rooms upon vacancy for signs of bed bugs as part of the cleaning routine. If bed bugs are found, under mattresses, box springs, and drapes should be removed from the room. Mattresses and box springs should be stored in zippered plastic covers isolated and stored offsite for one year to ensure the elimination of bed bugs.
Thorough cleaning and vacuuming should be done. Cracks in wallpapers, baseboards, or plaster should be filled/caulked prior to calling a professional exterminator. Travellers should only take what you will need for the trip. Inspect the room prior to bringing your luggage into the room.
Pack toiletries in plastic zip lock bags and take large plastic bags to store worn clothes. Do not place the suitcase on the floor. Before packing to leave the hotel, inspect your luggage for bed bugs, place all personal items in bags, then in the suitcases. When arriving home, leave your suitcases outside.
Remove objects and inspect for bed bugs; wash all clothing in hot water and high heat dryer setting. Non-washable items should be dry cleaned. Place your luggage in tightly sealed plastic bags and leave in the garage or outside the home.
Are there any restrictions for people with bed bugs?
Bed bugs usually feed at night and then drop off the host. People who live in an area infested with bed bugs do not have to be excluded from work or school, but they should not bring items outside the home, which could spread bed bugs to other places.
If items must be brought to school, like backpacks, they should be sealed in an airtight container while at school. Early detection and efficient treatment are crucial to controlling bed bug infestation.
Who is responsible for bed bugs, the landlord or the tenant?
Date: 14th of April 2023
